STATISTICS: MEDIAN 2(LECTURE 6)
Empirical Relation Between Mean, Median And Mode (Median 2)
Dear Students,
Q 2. The following table gives the frequency distribution of married women by age at marriage. calculate the median of the given data.
Note: The data needs to be converted to continuous classes for finding the median, since the formula assumes continuous classes.
Dear Students,
Good Morning Everyone!!
In the previous class we covered the following learning outcomes:
- How to find the median of grouped/ungrouped data by using formula.
Let us go through the guidelines for the blog once again:
• The text in Red, is to be written in your register
• The text in blue is to be viewed by clicking on it
• The text in green is to be practiced for home work
1. Take your SET-A mathematics register.
2. Our handwriting reflects a lot about us. It will be awesome if you use good presentation and cursive hand writing
3. Make a column on the right hand side, if you need to do any rough work
4. Write today's date on the line after that. We need to save paper.
Let us recall:
What is median?
Formula for finding the median of grouped data
Please write the learning outcomes as mentioned below:
Today I will be able to apply the empirical relationship between the three measures of central tendency.
How to calculate the frequency of a class interval if the median of the data is given.
Let us do this example:(Do it in the register)
Q 1. The median of the
following frequency distribution is 35. Find the value of x . Also find the
modal class.
|
Q 2. The following table gives the frequency distribution of married women by age at marriage. calculate the median of the given data.
AGE (IN YEARS)
|
FREQUENCY
|
15-19
|
53
|
20-24
|
140
|
25-29
|
98
|
30-34
|
32
|
35-39
|
12
|
Note: The data needs to be converted to continuous classes for finding the median, since the formula assumes continuous classes.
Empirical
Relation Between Mean, Median And Mode
A
distribution in which the values of mean, median and mode coincide (i.e. mean =
median = mode) is known as a symmetrical distribution. Conversely, when values
of mean, median and mode are not equal the distribution is known as
asymmetrical or skewed distribution. In moderately skewed or asymmetrical
distribution a very important relationship exists among these three measures of
central tendency. In such distributions the distance between the mean and
median is about one-third of the distance between the mean and mode Mode = mean
- 3 [mean - median]
Mode
= 3 median - 2 mean
Knowing
any two values, the third can be computed.
Example
Given median = 20.6, mode = 26 Find mean.
Given median = 20.6, mode = 26 Find mean.
Solution:
HOMEWORK: Complete exercise 14.3
AQAD
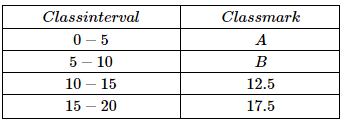
Q. Look at the following table below.

The value of A & and B respectively are:
a. 3,8
b. 2,7
c. 3,7
d. 2.5, 7.5







Good morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteAaron De Menezes
10-B
Good Morning ma'am
ReplyDeletegood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteyashvardhan chaudhary 10b
good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteaditya das
10-B
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSharad dubey
10b
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteDaksh Mahajan
10-B
Good morning ma'am.
ReplyDeleteYashwardhan Jha.
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDelete-Ian Saluja
good morning ma'am
ReplyDeletekrrish wadhawan
10-B
Good morning mam
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSatvik Ahuja
10B
Good Morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteSaumil Gupta
X-B
Good morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteKaran Bahadur
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteJason Kandir
10 B
Ans: AQAD
D) 2.5, 7.5
Vasav Aggarwal
ReplyDeleteXB
d is the answer to aqad
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteAnush Gupta
Stephen Sunny 10-B
ReplyDeleteGood morning Ma'am
ReplyDeleteKevin Toppo
10-B
Good morning ma'am.Harsh X-B
ReplyDeletegood morning
ReplyDeletemichael hyam
10 b
ans=d
GOOD MORNING MAM
ReplyDeleteDION DSOUZA
10B
good morning mam
ReplyDeleteanugrah singh
10 b
ans-d)
Good morning mam
ReplyDeleteBOAZ LEPCHA
10 B
Good morning mam
ReplyDeleteYashvardhan Singh
10B
Good morning mam
ReplyDeleteMandeep Singh
X-B
GOOD MORNING MA'AM
ReplyDeleteNAMAN MEHTA 10-B
Ma'am in the first question of class work, how to find n/2 w/o the total frequency given?
ReplyDeletenot necessary.............
DeleteGood Morning maam
ReplyDeleteAniket Sharma
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteGood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteGurkirat Singh
Good morning ma’am
ReplyDeleteJoe Mathew
X-B
Good morning
ReplyDelete10 b
Mam ans= d
ReplyDeleteMa’am in the first CW question, what is the total frequency?
ReplyDeleteGood morning maam
ReplyDeleteAnsh Aggarwal
10B
Total frequency is not required to answer this qn, if not take it as 30.
ReplyDeletegood morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteibrahim farooqui
10-B
Good morning mam .
ReplyDelete-Mohit Gogia 10-B
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteSanyam S Sahoo
10B
Aniruddha Majumdar
ReplyDelete10 B
Good morning ma'am
ReplyDeleteArshan khan
AQAD = option D..... 2.5 AND 7.5
ReplyDeleteKevin George 10B
ReplyDeleteChecking
ReplyDeleteMa'am how is it possible that we can find the solution of CW question 1 without knowing the value of n?
ReplyDeleteGood evening mam.. OANGSANG 😉
ReplyDelete